CPVC vs PVC Processing
Can We Use a PVC Machine for CPVC Production?
The CPVC process using extrusion and injection is very similar to the PVC process.
Additionally, you can typically use PVC equipment and tools in the CPVC manufacturing process. However, proper temperature settings, screws and molding tools are necessary.
What Is the Main Difference Between CPVC and PVC Processing?
The main difference between PVC and CPVC processing lies in thermal stability and viscosity.
If you don’t apply moderate temperatures and heat to CPVC, it won’t melt, and its physical properties won’t perform well. Hydrochloric acid decomposes when exposed to high temperatures. For reference, we’ve illustrated the crystalline melting points for PVC and CPVC below.
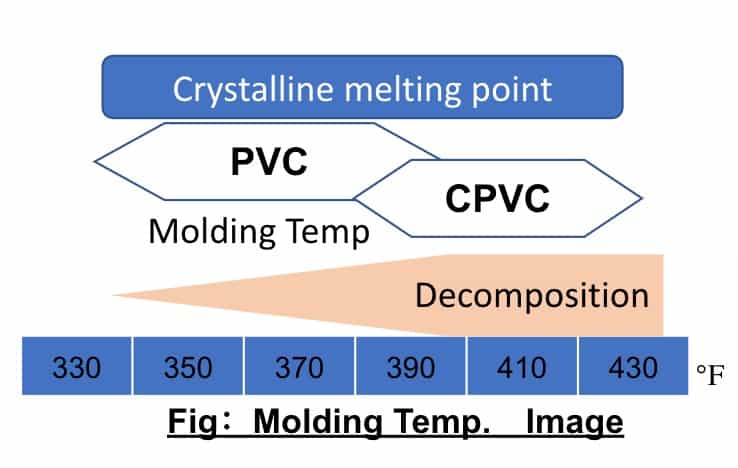
Can We Use a PVC Machine for CPVC Production?
Key Points
PVC and CPVC materials have different thermal stabilities:
- CPVC materials must reduce the residence time of the molding tools as much as possible.
- Resin temperature settings are important to ensure the material’s melting and gelation.
Viscosity (Fluidity)
Generally, CPVC’s viscosity is higher than that of PVC. You can simply read PVC’s viscosity as K-Value = Polymerization. For CPVC, you calculate viscosity (K-Value) by PVC polymerization degrees and chlorination degrees.
Key Points
- Motor load, back pressure
If back pressure is high and increasing production speed is difficult, the material will remain inside the die longer and burn. - Screw/mold shape
The structure of the screw and die tools is an important factor. You must match the tools with CPVC production. - Attention to shear heating
The screw undergoes shear heating. As a result, moderate heat is necessary to keep the plastic at the correct temperature.
Processing Differences Between CPVC vs. PVC
Extrusion Differences Between CPVC vs. PVC
| PVC | CPVC | ||
| Machine | Screw mortar:High torque Screw:Parallel φ60-170 Conical φ50-85 |
Screw mortar:High torque Screw:Parallel φ60-135 Conical φ50-70 |
|
| Condition | Screw Rotation | ー | Lower than PVC |
| Barrel Temp. | 300 – 340℉ | 340 – 410℉/span> | |
| Mold Type | Stainless steel chrome plate | Stainless steel chrome plate Less volume (residence part) Mold angle |
|
*We cannot guarantee these reference values.
Injection Differences Between CPVC vs. PVC
| PVC | CPVC | ||
| Machine | Screw mortar: High torque Barrel cooling: Blower |
Screw mortar: High torque Barrel cooling: Blower Barrel zone: 4-5 zone Nozzle: Short nozzle、φ:Larger than PVC |
|
| Condition | Screw Rotation | 9-14 m/sec | 8-13 m/sec (lower than PVC) |
| Barrel Temp. | 320 – 365℉ | 320 – 392℉ | |
| Holding Pressure | 100 – 170 MPa | 100 – 170 MPa | |
| Mold Type | Stainless steel chrome plate Runner: Thick Hot runner: No need Gate: Direct gate Wall thickness > gate diameter |
Stainless steel chrome plate Runner: Thick Hot runner: No need Gate: Direct gate Larger than PVC |
|
*We cannot guarantee these reference values.
Single Extruder (Profile) Differences Between CPVC vs. PVC
| PVC | CPVC | ||
| Machine | Single screw machine Screw: Dulmate, Fullfight |
Single screw machine Screw: Recommend Fullfight (Dulmate) L/D = 22 – 25 Compression ratio: 2.5 – 3.2 |
|
| Condition | Screw Rotation | 15~ rpm (65 mm single) | 15–25 rpm (65 mm single) |
| Barrel Temp. | 284 – 338℉ | 300 – 370℉ | |
| Mold Type | Stainless steel chrome plate | Stainless steel chrome plate | |
*We cannot guarantee these reference values.
